6 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
On Christmas Day in 1968, the three-man Apollo 8 crew of Frank Borman, Jim Lovell, and Bill Anders found a surprise in their food locker: a specially packed Christmas dinner wrapped in foil and decorated with red and green ribbons. Something as simple as a “home-cooked meal,” or as close as NASA could get for a spaceflight at the time, greatly improved the crew’s morale and appetite. More importantly, the meal marked a turning point in space food history.
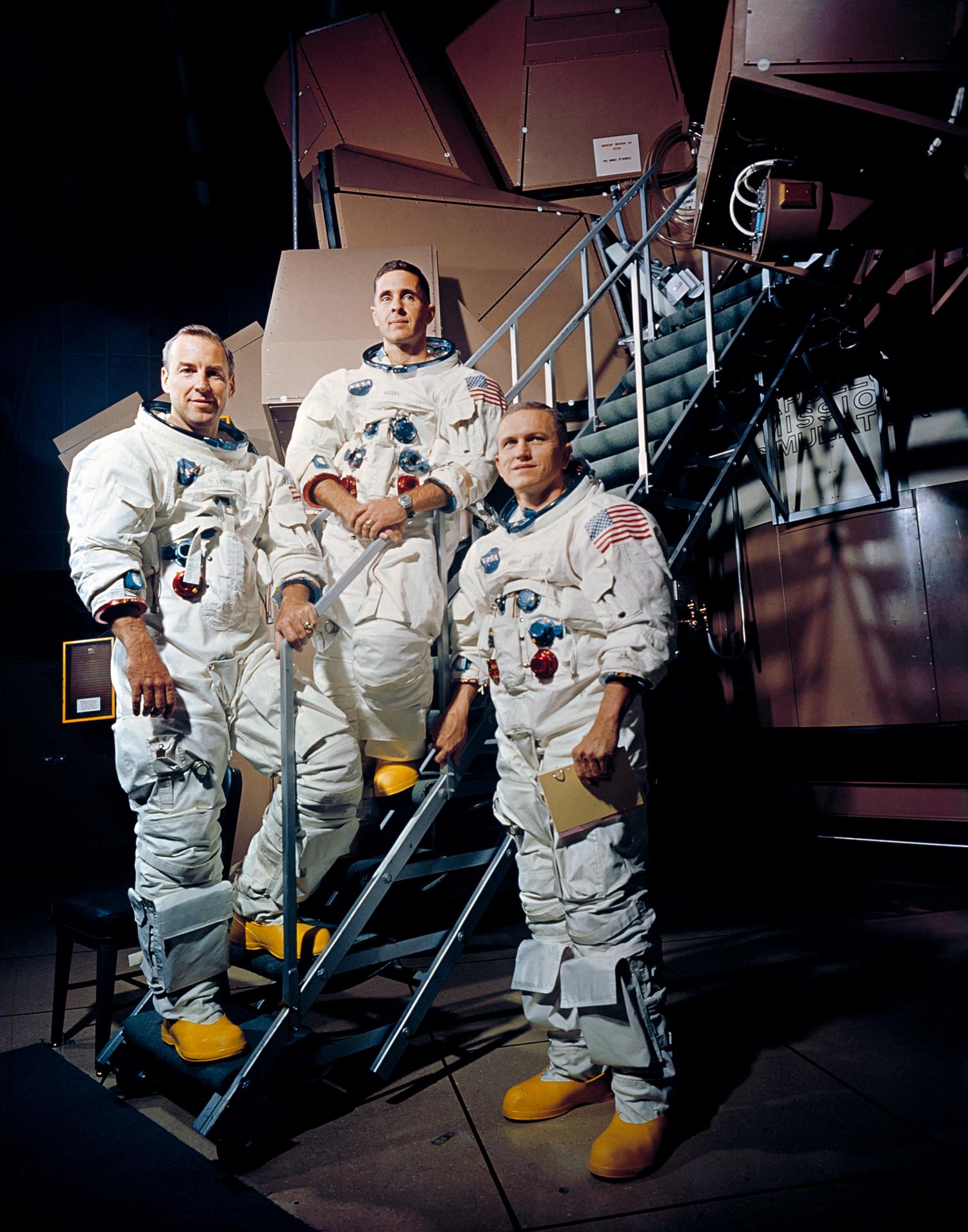

On their way to the Moon, the Apollo 8 crew was not very hungry. Food scientist Malcolm Smith later documented just how little the crew ate. Borman ate the least of the three, eating only 881 calories on day two, which concerned flight surgeon Chuck Berry. Most of the food, Borman later explained, was “unappetizing.” The crew ate few of the compressed, bite-sized items, and when they rehydrated their meals, the food took on the flavor of their wrappings instead of the actual food in the container. “If that doesn’t sound like a rousing endorsement, it isn’t,” he told viewers watching the Apollo 8 crew in space ahead of their surprise meal. As Anders demonstrated to the television audience how the astronauts prepared a meal and ate in space, Borman announced his wish, that folks back on Earth would “have better Christmas dinners” than the one the flight crew would be consuming that day.1
If that doesn’t sound like a rousing endorsement, it isn’t.

Frank Borman
Apollo 8 Astronaut
Over the 1960s, there were many complaints about the food from astronauts and others working at the Manned Spacecraft Center (now NASA’s Johnson Space Center). After evaluating the food that the Apollo 8 crew would be consuming onboard their upcoming flight, Apollo 9 astronaut Jim McDivitt penciled a note to the food lab about his in-flight preferences. Using the back of the Apollo 8 crew menu, he directed them to decrease the number of compressed bite-sized items “to a bare minimum” and to include more meat and potato items. “I get awfully hungry,” he wrote, “and I’m afraid I’m going to starve to death on that menu.”2
In 1969, Rita Rapp, a physiologist who led the Apollo Food System team, asked Donald Arabian, head of the Mission Evaluation Room, to evaluate a four-day food supply used for the Apollo missions. Arabian identified himself as someone who “would eat almost anything. … you might say [I am] somewhat of a human garbage can.” But even he found the food lacked the flavor, aroma, appearance, texture, and taste he was accustomed to. At the end of his four-day assessment he concluded that “the pleasures of eating were lost to the point where interest in eating was essentially curtailed.”3

Apollo 8 commander Frank Borman concurred with Arabian’s assessment of the Apollo food. The one item Borman enjoyed? It was the contents of the Christmas meal wrapped in ribbons: turkey and gravy. The Christmas dinner was so delicious that the crew contacted Houston to inform them of their good fortune. “It appears that we did a great injustice to the food people,” Lovell told capsule communicator (CAPCOM) Mike Collins. “Just after our TV show, Santa Claus brought us a TV dinner each; it was delicious. Turkey and gravy, cranberry sauce, grape punch; [it was] outstanding.” In response, Collins expressed delight in hearing the good news but shared that the flight control team was not as lucky. Instead, they were “eating cold coffee and baloney sandwiches.”4
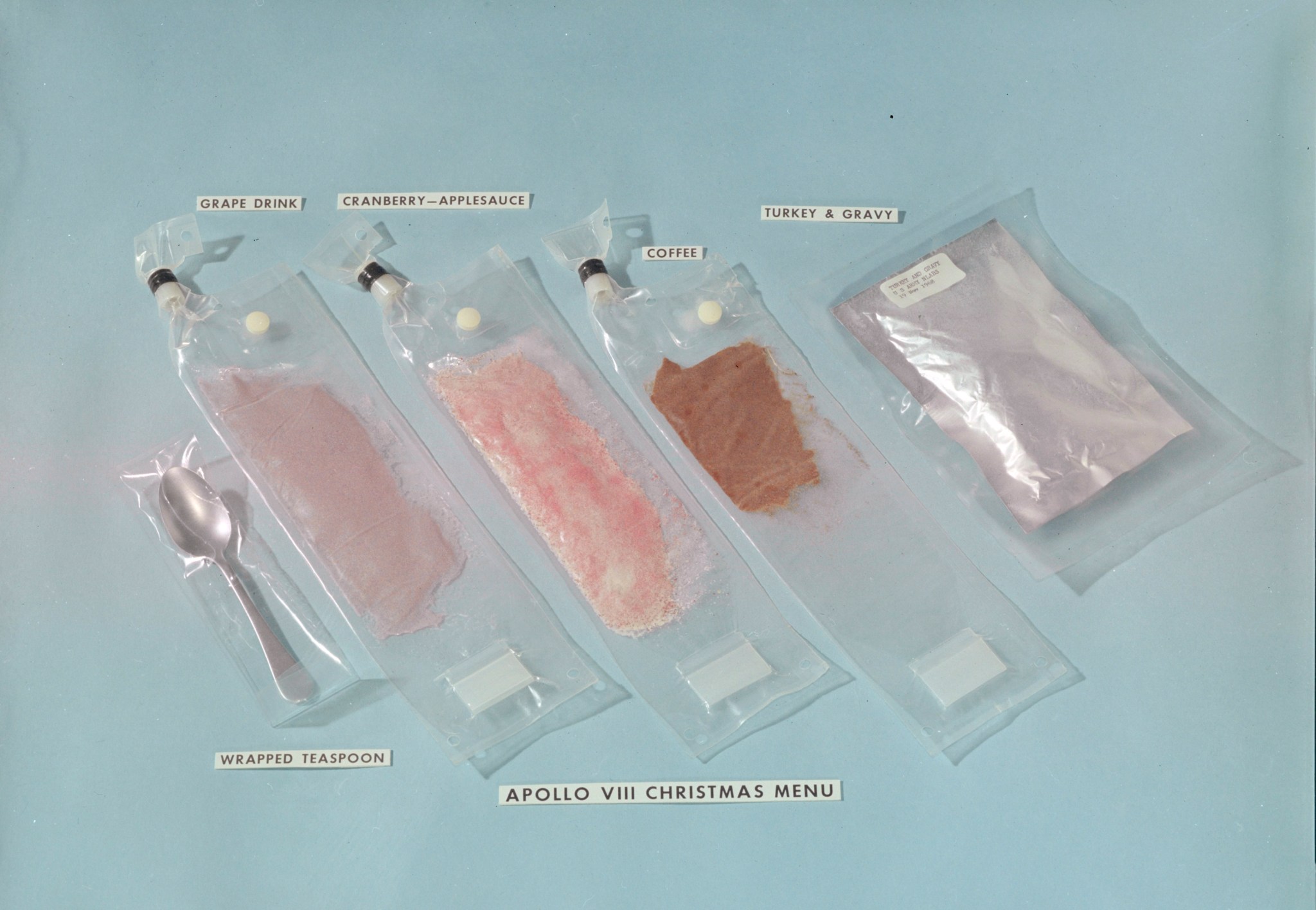

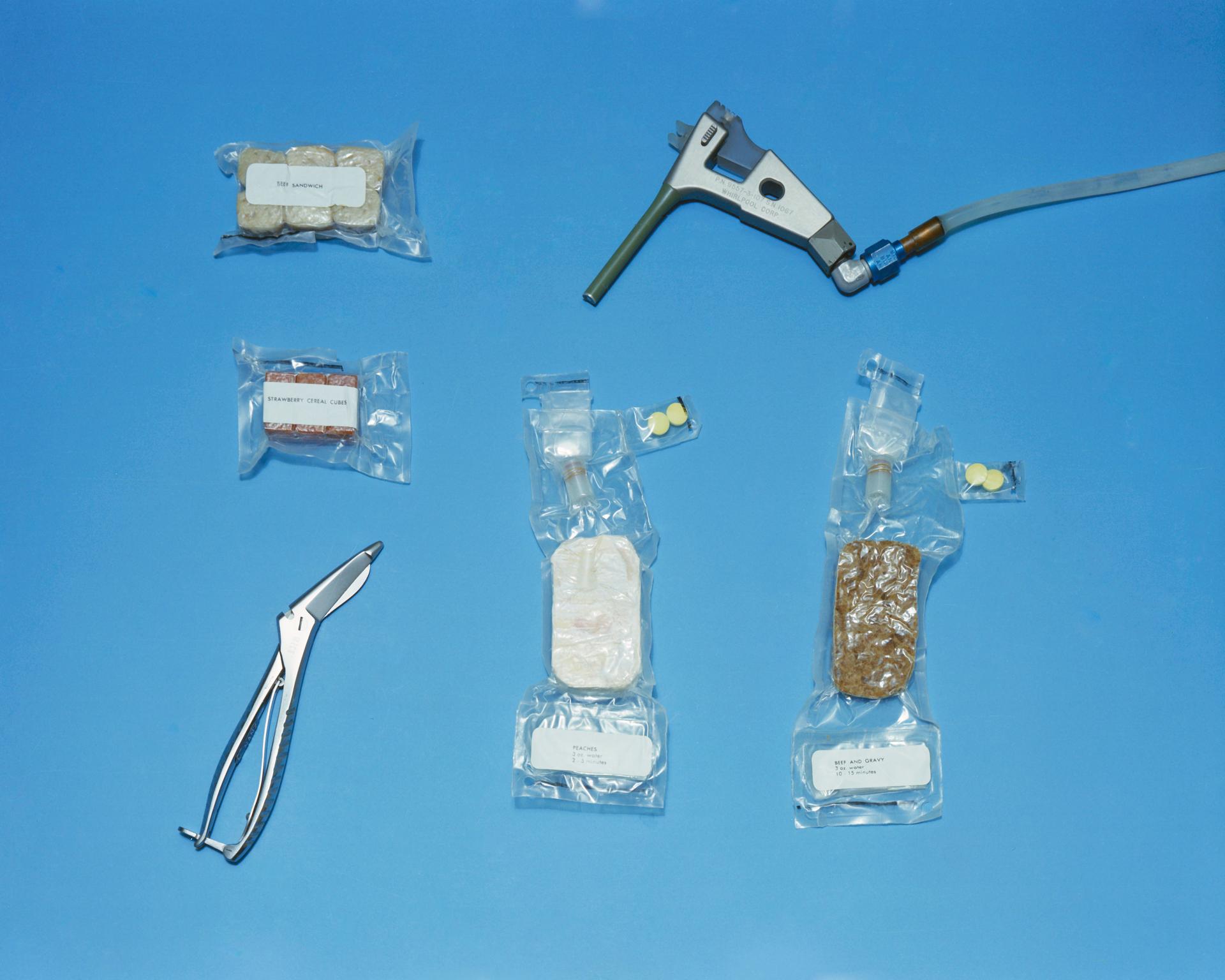
The Apollo 8 meal was a “breakthrough.” Until that mission, the food choices for Apollo crews were limited to freeze dried foods that required water to be added before they could be consumed, and ready-to-eat compressed foods formed into cubes. Most space food was highly processed. On this mission NASA introduced the “wetpack”: a thermostabilized package of turkey and gravy that retained its normal water content and could be eaten with a spoon. Astronauts had consumed thermostabilized pureed food on the Project Mercury missions in the early 1960s, but never chunks of meat like turkey. For the Project Gemini and Apollo 7 spaceflights, astronauts used their fingers to pop bite-sized cubes of food into their mouths and zero-G feeder tubes to consume rehydrated food. The inclusion of the wetpack for the Apollo 8 crew was years in the making. The U.S. Army Natick Labs in Massachusetts developed the packaging, and the U.S. Air Force conducted numerous parabolic flights to test eating from the package with a spoon.5
Smith called the meal a real “morale booster.” He noted several reasons for its appeal: the new packaging allowed the astronauts to see and smell the turkey and gravy; the meat’s texture and flavor were not altered by adding water from the spacecraft or the rehydration process; and finally, the crew did not have to go through the process of adding water, kneading the package, and then waiting to consume their meal. Smith concluded that the Christmas dinner demonstrated “the importance of the methods of presentation and serving of food.” Eating from a spoon instead of the zero-G feeder improved the inflight feeding experience, mimicking the way people eat on Earth: using utensils, not squirting pureed food out of a pouch into their mouths. Using a spoon also simplified eating and meal preparation. NASA added more wetpacks onboard Apollo 9, and the crew experimented eating other foods, including a rehydrated meal item, with the spoon.6
Food was one of the few creature comforts the crew had on the Apollo 8 flight, and this meal demonstrated the psychological importance of being able to smell, taste, and see the turkey prior to consuming their meal, something that was lacking in the first four days of the flight. Seeing appetizing food triggers hunger and encourages eating. In other words, if food looks and smells good, then it must taste good. Little things like this improvement to the Apollo Food System made a huge difference to the crews who simply wanted some of the same eating experiences in orbit and on the Moon that they enjoyed on Earth.
Footnotes
[1] Apollo 8 Mission Commentary, Dec. 25, 1968, p. 543, https://historycollection.jsc.nasa.gov/JSCHistoryPortal/history/mission_trans/AS08_PAO.PDF; Apollo 8 Technical Debriefing, Jan. 2, 1969, 078-15, Apollo Series, University of Houston-Clear Lake, Houston, Texas (hereafter UHCL); Malcolm C. Smith to Director of Medical Research and Operations, “Nutrient consumption on Apollo VII and VIII,” Jan. 13, 1969, Rita Rapp Papers, Box 1, UHCL.
[2] Jim McDivitt food evaluation form, n.d., Box 17, Rapp Papers, UHCL.
[3] Donald Arabian to Rapp, “Evaluation of four-day food supply,” May 8, 1969, Box 17, Rapp Papers, UHCL.
[4] Apollo 8 Mission Commentary, Dec. 25, 1968, p. 545.
[5] Malcolm Smith, “The Apollo Food Program,” in Aerospace Food Technology, NASA SP-202 (Washington, DC: 1970), pp. 5–8; Whirlpool Corporation, “Space Food Systems: Mercury through Apollo,” Dec. 1970, Box 9, Rapp Papers, UHCL.
[6] Smith, “The Apollo Food Program,” pp. 7–8; Smith to the Record, “Christmas Dinner for Apollo VIII,” Jan. 10, 1969, Box 1, Rapp Papers, UHCL; Smith et al, “Apollo Food Technology,” in Biomedical Results of Apollo, NASA SP-368 (Washington, DC: NASA, 1975), p. 456.
About the Author
Jennifer Ross-Nazzal
Jennifer Ross-Nazzal is the NASA Human Spaceflight Historian. She is the author of Winning the West for Women: The Life of Suffragist Emma Smith DeVoe and Making Space for Women: Stories from Trailblazing Women of NASA’s Johnson Space Center.